Federal Reserve Economic Data
- Release Calendar
- FRED Tools
- FRED News
- FRED Blog
- About FRED
Data in this graph are copyrighted. Please review the copyright information in the series notes before sharing.
Notes
Source: World Bank
Release: Global Financial Development
Units: Percent, Not Seasonally Adjusted
Frequency: Annual
Notes:
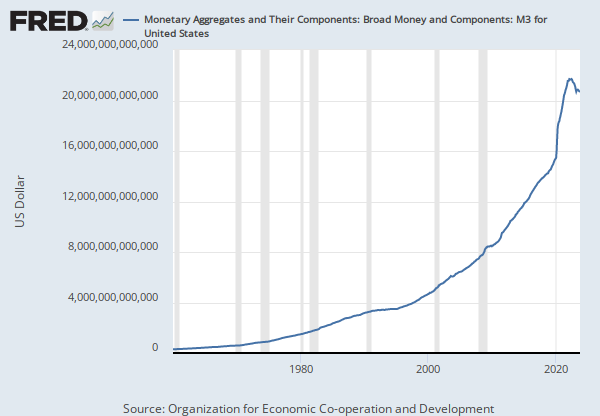
Ratio of liquid liabilities to GDP. Liquid liabilities are also known as broad money, or M3. They are the sum of currency and deposits in the central bank (M0), plus transferable deposits and electronic currency (M1), plus time and savings deposits, foreign currency transferable deposits, certificates of deposit, and securities repurchase agreements (M2), plus travelers checks, foreign currency time deposits, commercial paper, and shares of mutual funds or market funds held by residents.
Ratio of liquid liabilities to GDP, calculated using the following deflation method: {(0.5)*[Ft/P_et + Ft-1/P_et-1]}/[GDPt/P_at] where F is liquid liabilities, P_e is end-of period CPI, and P_a is average annual CPI. Raw data are from the electronic version of the IMF's International Financial Statistics. Liquid liabilities (IFS lines 55L..ZF or, if not available, line 35L..ZF); GDP in local currency (IFS line 99B..ZF or, if not available, line 99B.CZF); end-of period CPI (IFS line 64M..ZF or, if not available, 64Q..ZF); and annual CPI (IFS line 64..ZF). For Eurocurrency area countries (BEF, DEM, ESP, FRF, GRD, IEP, ITL, LUF, NLG, ATS, PTE, FIM), liquid liabilities are estimated by summing IFS items 34A, 34B and 35. (International Monetary Fund, International Financial Statistics, and World Bank GDP estimates)
Source Code: GFDD.DI.05
Suggested Citation:
World Bank, Liquid Liabilities to GDP for Zimbabwe [DDDI05ZWA156NWDB], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/DDDI05ZWA156NWDB, .
Release Tables
Related Data and Content
Data Suggestions Based On Your Search
Content Suggestions
Related Categories
Releases
Tags
Permalink/Embed
modal open, choose link customization options
Select automatic updates to the data or a static time frame. All data are subject to revision.